



scientific research on caapi’s brain benefits.
Cognitive Function
Compounds in Caapi increase the availability of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, potentially enhancing cognitive function and offering protection against neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer's by promoting neuron survival and preventing the buildup of harmful proteins.
Mood Regulation
Compounds in Caapi selectively inhibit serotonin reuptake, leading to increased serotonin levels that may facilitate mood stability, reduce anxiety, and help manage symptoms of stress and depression, making it potentially beneficial for mood disorders and conditions related to serotonin dysregulation, such as anxiety and PTSD.
Neuroprotection
Compounds in Caapi act as mild stimulants for the central nervous system, which may enhance alertness and protect neurons. This could offer potential benefits in conditions such as Parkinson's disease by reducing oxidative stress and preserving dopaminergic neurons, helping to support long-term brain health
Caapi extract contains active alkaloids, Harmine,Harmaline and Tetrahydroharmine
Mood Regulation
Tetrahydroharmine selectively inhibits serotonin reuptake, leading to increased serotonin levels that can facilitate mood stability, reduce anxiety, and help manage symptoms of stress and depression.
, making it potentially beneficial for mood disorders and conditions related to serotonin dysregulation, such as anxiety and PTSD.
Neuroprotection
Harmaline acts as a mild CNS stimulant, which may enhance alertness and protect neurons, offering potential benefits in conditions such as Parkinson's disease by reducing oxidative stress and preserving dopaminergic neurons.
Cognitive Function
Harmine enhances the availability of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, potentially improving cognitive function and protecting against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's. by promoting the survival of neurons and inhibiting harmful protein aggregation.
Cognitive Function
Harmine enhances the availability of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, potentially improving cognitive function and protecting against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's.
by promoting the survival of neurons and inhibiting harmful protein aggregation.
Scientific research on caapi's brain benefits
Published scientific research shows Caapi's compounds could help build your brain's resilience against various stressors, and neurodegenerative diseases
The primary active compounds in Banisteriopsis caapi are beta-carboline alkaloids harmine, harmaline, and tetrahydroharmine (THH).
HARMINE
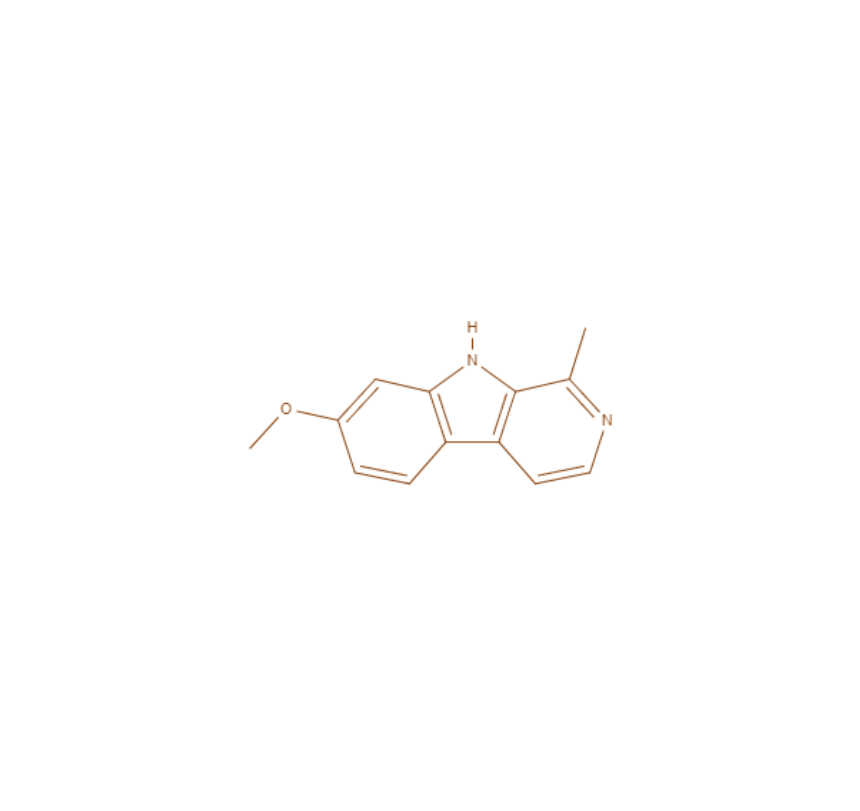
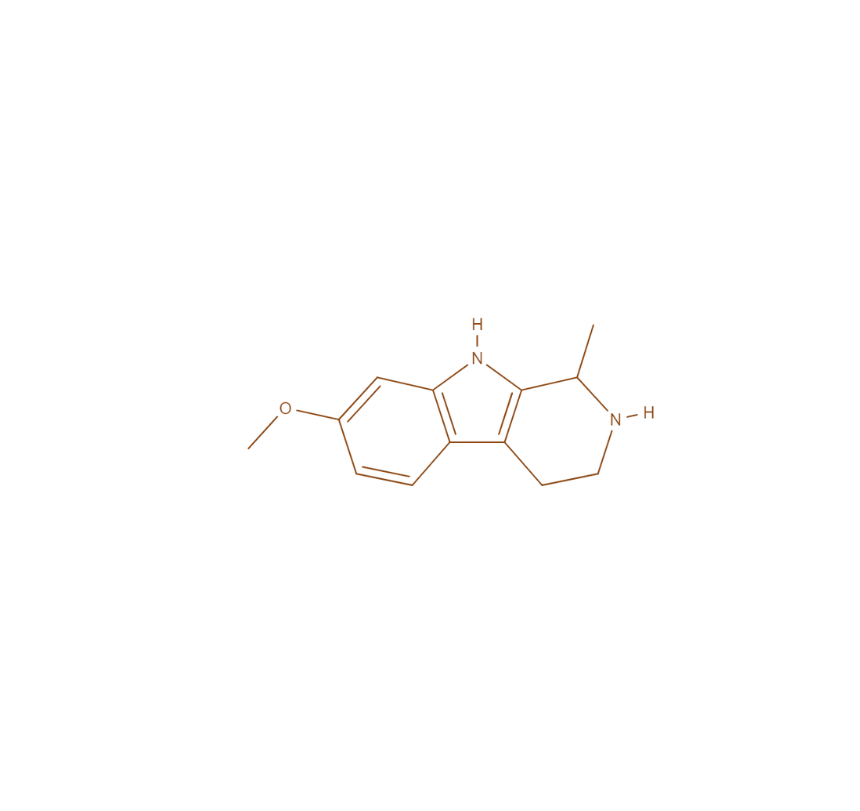
THH
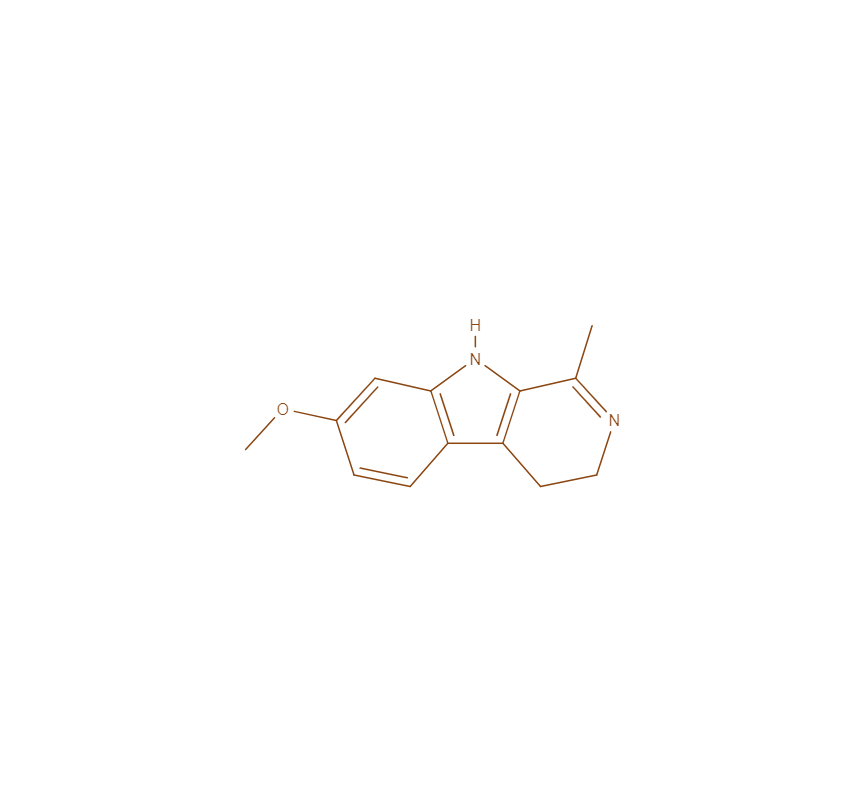
HARMALINE
Harmine has been shown to potentially protect neurons, enhance cognitive function, and stimulate neurogenesis.
It promotes neurogenesis by directly stimulating the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). BDNF plays a vital role in neuron survival and growth, and its increased expression is linked to enhanced neuroplasticity and the formation of new neural connections, especially in brain regions associated with learning and memory, like the hippocampus.
Harmaline has potential antidepressant effects by inhibiting the enzyme monoamine oxidase.
This can lead to an accumulation of neurotransmitters in synaptic spaces, enhancing communication between neurons and promoting mood stability. This mechanism helps alleviate symptoms of depression by preventing the degradation of these mood-regulating chemicals, leading to prolonged neurotransmitter action in the brain.
Tetrahydroharmine is a compound that regulates key neurotransmitters such as serotonin.
It acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI), which increases serotonin availability in the brain by preventing its reabsorption into neurons. This elevated serotonin level helps stabilize mood
The Research on caapi alkaloids
These studies delve into how these unique compounds interact with our brain, revealing potential benefits for cognition and mental health.
Effects on Cognitive function
Cognitive Enhancement
Harmine, an alkaloid in caapi vine has shown to stimulate neuroplasticity and optimize neurotransmission, which in turn may improve cognitive functions [1]. Harmine has also been studied for its potential benefits in Alzheimer's disease, showing improvements in memory and cognitive dysfunction. [2] Further preclinical evidence suggests harmine modulates memory processes and hippocampal function that can enhance memory. [3] Caapi vine functions as a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) which could influence cognitive functioning positively. {4}
Neuroprotection
Alkaloids found in Caapi vine might have significant benefits for treating neurodegenerative disorders [5]. By potentially shielding neurons from degeneration, caapi vine may play a significant role in alleviating symptoms and slowing down the progression of Parkinson's disease. [6} Further studies indicate these alkaloids induce anti-inflammatory effects in microglial cells, potentially providing central support for neuroprotective responses [7].
Neurogenesis
Caapi vine alkaloids could stimulate adult neurogenesis in vitro, meaning that they helped generate new neurons in brain cell cultures[8]. This suggests that these alkaloids could potentially support brain disorders by encouraging the development of new neural connections[6].
Patients become aware of personal reasons behind addictive behaviour in clinical study -The use of banisteriopsis caapi alone in application to drug addiction therapy.

The study
In a research study conducted at Takiwasi - centre for the rehabilitation of drug addicts and reasearch on traditional medicine; it was found that Banisteriopsis caapi shows potential beneficial contribution in treatment of substance use disorders.
What is substance use disorder?
Substance Use Disorder (SUD) is a medical condition characterised by an individual's inability to control their use of a substance, such as alcohol, despite the harmful consequences it may cause. SUD is linked with dysregulation in neurotransmitter systems, especially those involving dopamine and serotonin. SUD can range from mild to severe and is often associated with a variety of physical, psychological, and social problems.
The Science
Dopamine is said to be connected to the brain's reward system, which can play a crucial role in addiction. By acting as MAOIs, alkaloids in Banisteriopsis caapi can increase the levels of serotonin and dopamine in the brain by preventing their breakdown. This can help restore balance in these neurotransmitter systems. Research sugguests rhat stabilising neurotransmitter levels may alter the way the brain processes reward and reinforcement; leading to reduced cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
Effects on Mood
Antidepressant Effects
Harmine has shown some great potential in dealing with depression. It works by modulating neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine [1]- key players in how mood is regulated. Continuous use of harmine has been observed to have antidepressant-like effects [1], with studies suggesting harmine administration can mitigate anhedonic behaviour. [3] (The absence of joy, motivation and interest, often induced from chronic stressful situations. )
Mood regulation
Harmine has shown to increase brain derived neurotropic factor (BDNF) [4]. Studies indicate stress decreases the expression of BDNF and low levels of BDNF were observed in depressed subjects. [5] Further studies in drug addiction therapy, highlighted that harmine affects dopamine neurotransmission ; which can influence emotional states and aid in emotional regulation. [6] This provides promising insights into psychological therapeutic benefits. Research in cultural contexts additionally reveal use of Caapi vine can enhance empathy, according to reports from Piaroa shamans [7].



A landmark human study shows the effects of Banisteriopsis caapi extract in alleviating symptoms of Parkinson's disease.

.png)

